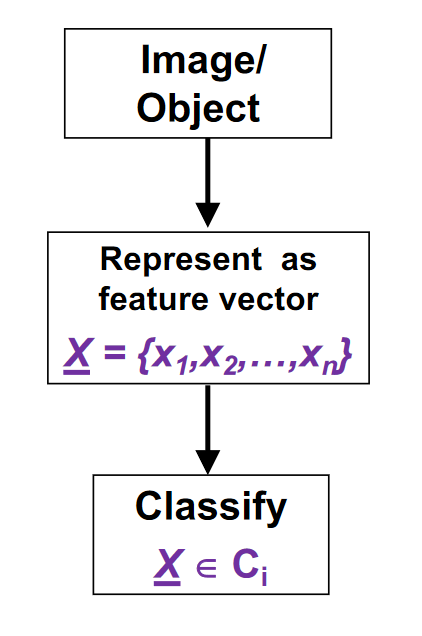
The study of pattern recognition deals with techniques such as automatic recognition or the identification of images or elements of images. Pattern recognition means that a computer is able to respond to stimuli from an external world through the medium of sensors.
Humans are great at pattern recognition without even trying:
- Recognising faces.
- Understanding written text.
- Navigating through physical spaces.
- Hand eye coordination.
- Identification of food.
Pattern recognition aims to provide computers with this intelligence.
Image pattern recognition also provides many applications:
- Medical Image analysis
- (Early signs of cancers)
- Xray anomalies
- Text Analysis
- Self-driving cars
- etc.
Definitions:
-
Pattern
-
Description of some object or entity in terms of the existence of identifying characteristics.
-
A pattern is represented as a [[feature vector]] where each element x represents a [[Feature]] or pattern descriptor.
-
We use data and make measurements to define patterns.
-
-
Pattern Recognition
- Overall process which allows the naming of a general category of object in response to data which form a specific pattern
-
Pattern Class
- Category determined by some common attributes among its members
- The same object or entity may be categorised in different ways. Often depending on the application of interest.
- Classes may be labelled in different ways:
- Specifically: C1='A', C2='B'
- Broadly defined: C1 = Normal, C2 = Abnormal
-
Feature
- (Pattern descriptor): a measurable property of a pattern selected to contribute to its identification
Pattern Recognition Task