Humans have a sophisticated vision system, with specialised cells that are able to detect meaningful features, organised hierarchically, and able to handle different aspects of vision.
As computer scientists, we aim to imitate this through machinery.
- Sensors will be required.
- Combining several simple components to form sophisticated processes.
- Encoding of information to match processing structure.
- Able to detect meaningful features to detect the structure of the real world, as we humans see it.
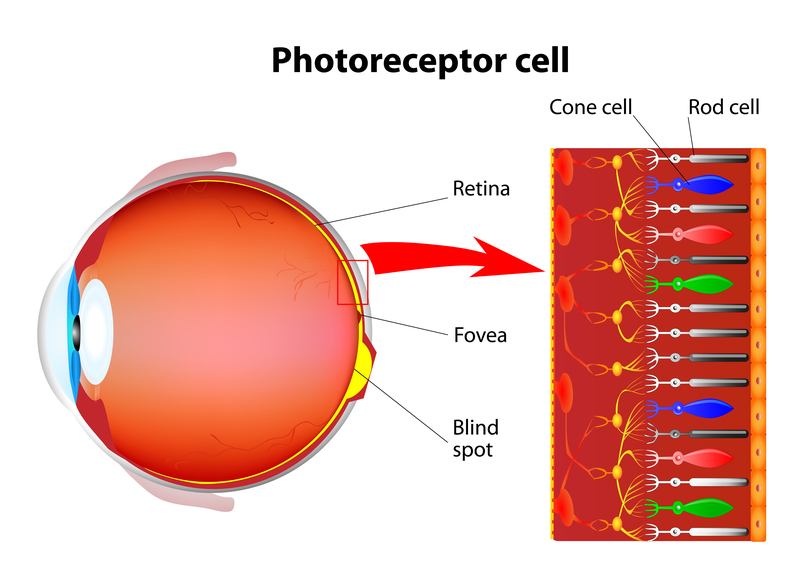
There are two types of photoreceptor cells: rods and cones.
- Rods function in dim light and provide black and white vision.
- Cones function in daytime vision and have the perception of colour.
Aquisition of images
Many sensors are available, typical reflection of light to xray imaging. However, the resulting image can only be a tranformed representation that a computer is able to understand and manipulate.
- There are a number of different representations, and compression strategies to be able to represent higher detailed imagery, with smaller storage use.
One Typical digital imaging process:
Image Representation
An image is a 2D intensity function. For grayscale images this is simply.
$$ f(x,y) = 0 - 255 $$ Whilst a coloured image may be a combination of several colours to form a pixel intensity.
Amplitude Digitisation
For black and white imagery, this would be measuring the brightness / energy of each individual pixel of the image.
- Uses a predetermined range of numbers (Gray Level)
- G Level lays on a gray scale:
- Gmin = 0 (Darkest)
- Gmax = G - 1 (Lightest)
- For a common hexadecimal value. This would be 0 (Black) - 255 (White)
Image Properties
N and G are two important properties of an image.
- Resolution: Degree of detail of an image is dependent on relation between N and G.
- Storage Requirements: The number of bits (B) required to represent an image.
- $$ G = 2^m$$
- $$ B = N^2 m$$
Effects from Digitisation
- Pixelation:
- Lost detail. Blocky effect of an image.
- False Contour:
- False detail created, usually when trying to create shades of imagery, may introduce structure to an image, which might just be a shading element.
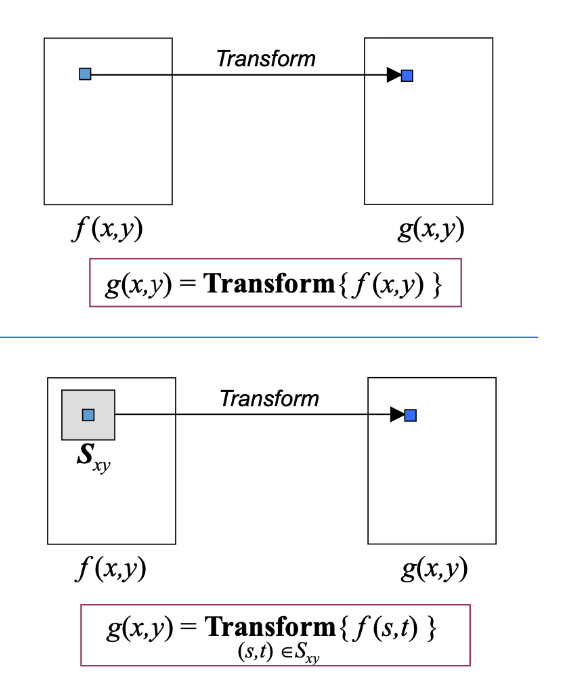
Point vs Neighborhood Operations
-
Point operation:
- transformation is a direct mapping of a single pixel to another pixel value.
-
Neighborhood operation:
- Transformation involves a spatial range of a pixel to determine new pixel value of the operation
Types of images
- Binary Image:
- Pixels represented as binary strings.
- Gray scale image:
- Pixels represented via gray level.
- For most image processing and analysis, grayscale is enough to represent structural detail and gather information from that a computer is able to process.
- Colour is often just for additional human interpolation.
- Colour image:
- Pixels represented as a combination of RBG.
Aquiring Coloured Images
-
Three CCD (Charge Coupled Device Arrays)
- Separating Red, Green, Blue components of an image through dichoic (thin colour filter that selectively passes a specific colour of light.) filters.

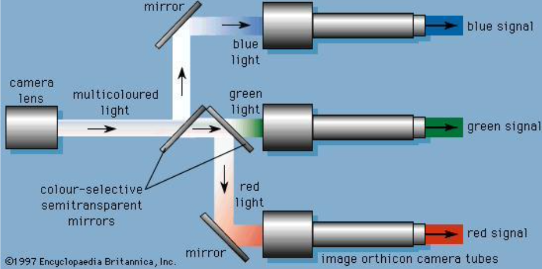
- Separating Red, Green, Blue components of an image through dichoic (thin colour filter that selectively passes a specific colour of light.) filters.
-
Colour filter array (Bayer Filter)
- a colour filter array for arranging RGB colour on a square grid of photosensors.
- Often used in digital cameras

-
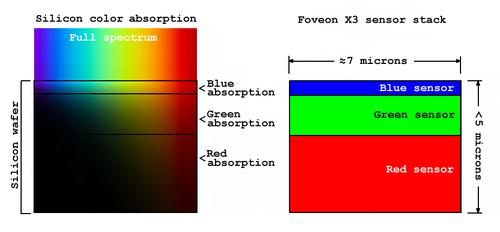
Foveon X3 sensor
- An array of photosites, which each include three vertically stacked photodiodes
- As different wavelengths of light penetrate the silicone differently, can use this effect to determine colours used.
- There is not a specific RGB chambers, so colours produced are identical to measured wavelengths.
- Produced full colour image
Goals of image processing
Image processing can be used to improve the visual appearance of digital imagery for human interpolation.
- Contrast enhancement
- image sharpening
- Noise removal
Image processing can also provide a benefit by creating structural features of an image to be made more obvious. Aspects of vision such as edge detection is able to be made so much more visual through computer enhancements.
- Edge detection
- Segmentation of an image
- Image compression (Reducing storage use of an image, whilst retaining visually identical information)